Top 7 COVID Updates You Should Know Come Election Day
Description
In this video, I discuss updates with the COVID surge that is here, controlling the COVID Pandemic, Immunity to the Coronavirus, possible Coronavirus treatments on the horizon, and more.
Timestamps:
00:00 Introduction of Top 7 COVID Updates
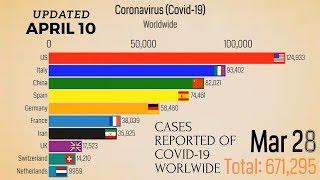
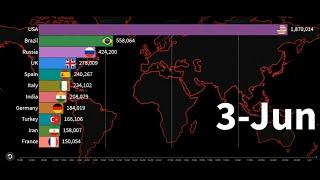
01:17 Surge in COVID Cases
02:24 Coronavirus Pandemic Control
03:45 Doctors Inflate Numbers
05:31 Coronavirus Immunity
06:34 COVID Vaccine
07:23 Aspirin for COVID
08:24 Coronavirus Treatment
And as if COVID by itself is not bad enough, it has a domino effect on the rest of our society. It's not just the economy that suffers. It’s also the rest of healthcare in general that suffers. Not to mention increased rates of depression and suicide deaths during these times. If hospitals are overwhelmed, guess what happens to the care of other patients who don’t have COVID? Cancer treatment becomes delayed.
Elective surgeries are being put off for things like heart surgery, hip replacement, and more. Also, who wants to go to a doctor's office, or an ER during these times, and possibly get COVID? It’s not like we don’t know how to get this pandemic under control. It can be done. Look at how well other countries handled it, and how well they are doing. And how well their economies are doing. Australia. New Zealand. South Korea. Taiwan. What do all of these countries have in common? Testing, contact tracing, quarantine, distancing, and masks.
This pandemic is only going to get worse in the next couple of months, and more and more hospitals will be overwhelmed. The difference between what's happening now compared to what happened during the previous spike in cases is that the entire country is a hotspot. And because it is so widespread, we will soon reach a breaking point in our hospitals and the number of healthcare workers.
In all likelihood, one of three things is going to happen. One, there will be a federal mask mandate, because not enough people are wearing masks when they should be. If this does not happen, there will likely be a shutdown of most of the country. If neither of these things happens, it will be millions of deaths and an absolutely destroyed economy.
Now some people say, doctors are inflating the numbers. So this is not true. Part of my job as an ICU physician is to complete a death certificate, and I have to write the primary cause of death and secondary causes of death. There is usually a chain of events that causes someone to die. Lots of times, there are multiple contributing factors that lead to someone’s death, but usually, we know the primary cause of death. And with COVID, it's usually pretty straight forward. Also, regarding the claim that doctors get paid more based on the diagnosis? It’s a lie, plain and simple.
Are people immune to the virus after they are infected? Antibodies are made by the body in response to a given infection or a vaccine. Usually, antibodies protect someone from future infection, and so they are called “neutralizing antibodies”. Researchers at Mount Sinai's Health System between March and October looked at the antibody responses of more than 30,000 people who tested positive for Coronavirus. These people who had Coronavirus had either mild or moderate illness.
In the study, they described their antibody responses as either low, moderate, or high. More than 90% had moderate to high levels of neutralizing antibodies to the spike protein of the virus, and the response was maintained for at least 5 months. So can you get infected with Coronavirus twice? Based on this, probably not. If it does occur, it’s the exception, not the rule. And this study also has implications when it comes to immunity from a vaccine. It’s likely that a vaccine will provide immunity, but for how long is another question. Based on this study, the answer is most likely at least 5 months.
There are over 70 monoclonal antibody treatments for COVID in various stages of development. The two that have the most potential right now are the ones made by Eli Lilly and Regeneron. Both of these companies have already applied for FDA emergency use authorizations. Eli Lilly recently signed a $375 million deal with the government for 300,000 vials of this monoclonal antibody, called Bamlanivimab. There was a recent study in NEJM that looked at Bamlanivimab, and it seemed to decrease the risk of hospitalization and ease some symptoms in this phase 2 trial that involved over 400 patients with either mild to moderate COVID.
In this RCT, less than 2% of patients who received Bamlanivimab had symptoms progress enough to the point of requiring hospitalization or a trip to the ER. For those who received a placebo, it was 6%. For patients in higher-risk categories – defined as those who were obese or older than 65 years - 4% who got the treatment were hospitalized, compared to 15% in the placebo group. The primary goal of the study was to see if the treatment eliminated the virus by day 11, which it did for the vast majority of patients.











![NEW Election, Covid & Stimulus Update [Mid 11-6]](https://no-mar.com/uploads/thumbs/605d0d29c-1.jpg)

![STIMULUS, Covid, & Election Update [11-3]](https://no-mar.com/uploads/thumbs/594e7aa7f-1.jpg)





Comments