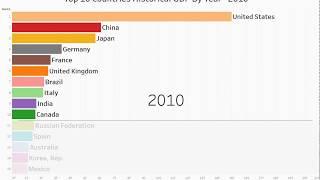
Top 10 Country GDP Ranking History (1960-2020) - Animated Running Graphs !
Description
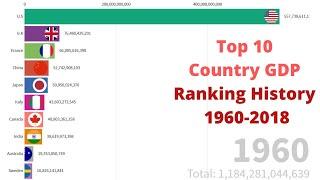
Top 10 Country GDP Ranking History (1960-2020). This country GDP ranking includes countries such as, United States, China, Japan, Germany, United Kingdom, etc.
Learn- How To Make A $100 A Day From Home Easily [For Every Country] in 2020 Year!
https://youtu.be/01AScVx1hlE
(Click above link)
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the monetary market value of all final goods and services made within a country during a specific period. GDP helps to provide a snapshot of a country’s economy and can be calculated using expenditures, production, or incomes.
World GDP
The world GDP is the added total of the gross national income for every country in the world. Gross national income takes a country’s GDP, adds the value of income from imports, and subtracts the value of money from exports. The value of gross national income, GNI, differs from that of GDP because it reflects the impact of domestic and international trade.
When the GNIs of every country in the world are added together, the value of imports and exports are in balance. The world economy consists of 193 economies, with the United States being the largest.
According to the International Monetary Fund, these are the highest ranking countries in the world in nominal GDP:
United States (GDP: 20.49 trillion)
China (GDP: 13.4 trillion)
Japan: (GDP: 4.97 trillion)
Germany: (GDP: 4.00 trillion)
United Kingdom: (GDP: 2.83 trillion)
France: (GDP: 2.78 trillion)
India: (GDP: 2.72 trillion)
Italy: (GDP: 2.07 trillion)
Brazil: (GDP: 1.87 trillion)
Canada: (GDP: 1.71 trillion)
United States
The United States has been the world’s largest economy since 1871. The nominal GDP for the United States is $21.44 trillion. The U.S. GDP (PPP) is also $21.44 trillion. Additionally, the United States is ranked second in the world for the approximate value of natural resources. In 2016, the U.S. had an estimated natural resource value of $45 trillion.
Several factors contribute to the U.S.’s powerful economy. The U.S. is known globally for cultivating a society that supports and encourages entrepreneurship, which encourages innovation and, in turn, leads to economic growth. The growing population in the U.S. has helped diversify the workforce. The U.S. is also one of the leading manufacturing industries in the world, coming only second to China. The U.S. dollar is also the most widely used currency for global transactions.
China
As the second-largest economy in the world, China has seen an average growth rate of 9.52% between 1989 and 2019. China is the second-largest economy considering nominal GDP, at $14.14 trillion, and the largest using GDP (PPP), which is $27.31 trillion. China has approximately $23 trillion in natural resources, 90% of which are rare earth metals and coal.
Japan
Japan has the third-largest economy in the world with a GDP of $5.15 trillion. Japan’s GDP (PPP) is $5.75 trillion. Japan’s economy is market-driven so businesses, production, and prices shift according to consumer demand, not governmental action. While the 2008 financial crisis took a hit on the Japanese economy and has stunted its growth since then, it is expected that the 2020 Olympics will give it a boost.
Germany
The German economy is the fourth-largest in the world with a GDP of $4.0 trillion. Germany has a GDP (PPP) of $4.44 trillion and a per capita GDP of $46,560, the 18th –highest in the world. Germany’s highly developed social market economy is Europe’s largest and strongest economy and has one of the most skilled workforces. According to the International Monetary Fund, Germany accounted for 28% of the euro area economy.
India
India’s economy is the fifth-largest in the world with a GDP of $2.94 trillion, overtaking the UK and France in 2019 to take the fifth spot. India’s GDP (PPP) is $10.51 trillion, exceeding that of Japan and Germany. Due to India’s high population, India’s GDP per capita is $2,170 (for comparison, the U.S. is $62,794). India’s real GDP growth, however, is expected to weaken for the third straight year from 7.5% to 5%.
India is developing into an open-market economy from its previous autarkic policies. India’s economic liberalization began in the early 1990s and included industrial deregulation, reduced control on foreign trade and investment, and privatization of state-owned enterprises. These measures have helped India accelerate economic growth. India’s service sector is the fast-growing sector in the world accounting for 60% of the economy and 28% of employment. Manufacturing and agriculture are two other significant sectors of the economy.
















Comments