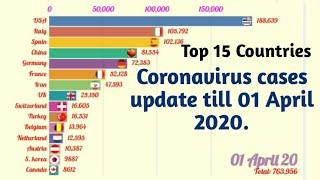
World Race To 1 Million Coronavirus Cases - Top 10 Countries (22nd Jan - 2nd April 2020) COVID19
Description
This is the race of the 10 countries in the #world ranked by most confirmed cases of #coronavirus #COVID19 infections from 22 January 2020 to 02 April 2020. You can observe how the number of confirmed coronavirus cases increased across the world to reach 1 Million mark.
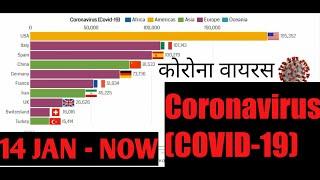
The 2019–20 coronavirus pandemic is an ongoing pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The outbreak started in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China, in December 2019. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the outbreak to be a Public Health Emergency of International Concern on 30 January 2020 and recognised it as a pandemic on 11 March 2020. As of 3 April 2020, more than 1,040,000 cases of COVID-19 have been reported in more than 190 countries and 200 territories, resulting in more than 55,100 deaths. More than 221,000 people have recovered.
The virus is mainly spread during close contact, and by small droplets produced when people cough, sneeze, or talk. These small droplets may be produced during breathing but the virus is not generally airborne. People may also catch COVID-19 by touching a contaminated surface and then their face. It is most contagious when people are symptomatic, although spread may be possible before symptoms appear. The time between exposure and symptom onset is typically around five days, but may range from 2 to 14 days. Common symptoms include fever, cough, and shortness of breath. Complications may include pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome. There is no known vaccine or specific antiviral treatment. Primary treatment is symptomatic and supportive therapy. Recommended preventive measures include hand washing, covering one's mouth when coughing, maintaining distance from other people, and monitoring and self-isolation for people who suspect they are infected.
Efforts to prevent the virus spreading include travel restrictions, quarantines, curfews, workplace hazard controls, event postponements and cancellations, and facility closures. These include national or regional quarantines throughout the world (starting with the quarantine of Hubei), curfew measures in mainland China and South Korea, various border closures or incoming passenger restrictions, screening at airports and train stations, and outgoing passenger travel bans.
The pandemic has led to severe global socioeconomic disruption, the postponement or cancellation of sporting, religious, and cultural events, and widespread fears of supply shortages resulting in panic buying. Schools and universities have closed either on a nationwide or local basis in more than 160 countries, affecting more than 1.5 billion students. Misinformation about the virus has spread online, and there have been incidents of xenophobia and discrimination against Chinese people and people of East Asian and Southeast Asian descent, and increasingly against people from other international hotspots as the pandemic spreads around the globe.







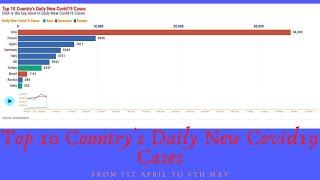
![Coronavirus Graph: Daily Confirmed Coronavirus Cases Per Million | Bar Chart Race [Updated 30 Jun]](https://no-mar.com/uploads/thumbs/6dfb3fb87-1.jpg)










Comments